Given a non-empty binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array.
Example 1:
Note:
The range of node's value is in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
解法1:
一个bfs解决问题。
要注意的是当中的加和可能会overflow,要用long。
C++
Java
Given a non-empty binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array.
Example 1:
Note:
The range of node's value is in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
一个bfs解决问题。
要注意的是当中的加和可能会overflow,要用long。
C++
Java
Given a set of distinct positive integers, find the largest subset such that every pair (Si, Sj) of elements in this subset satisfies: Si % Sj = 0 or Sj % Si = 0.
If there are multiple solutions, return any subset is fine.
Example 1:
nums: [1,2,3]
Result: [1,2] (of course, [1,3] will also be ok)
Example 2:
nums: [1,2,4,8]
Result: [1,2,4,8]
思路是:
if a < b then a % b != 0 for all a , b > 0
所以只需要对与一个数,只要从大往小找小于他的数即可。
第二步:
先把数组排序,便于分析。
对于排好序的数组,我们可以计算出对于每一个数字,数组中存在的可以整除他的数的最大个数。
这可以用一个dp完成。
统计出最大的个数的同时,如果我们维护另外一个数组,记录能被整除且sequence最长的那个数的index,就能在之后把整条链提取出来。
C++
Java
这题如果改成,求最长的subset的长度,使得subset中每两个数字都能保证其中一个被整除,那么这就是一个经典的dp问题。
这题的难点是在这个的基础上要求出这个subset。对于这种问题,一般可以采取的方法就是在dp的过程中记录下每一个点的optimal解法相对应的位置。
这题就是这样,dp[i]记录下对于第i个点,他们之前的0到i-1个点对应的能被其整除的数字的个数,当这个个数被更新的时候,记录下其所对应的位置。
当扫描结束一遍之后,我们也得到了对应于最大答案的subset中每一个点的位置。
|
|
Given two non-empty binary trees s and t, check whether tree t has exactly the same structure and node values with a subtree of s. A subtree of s is a tree consists of a node in s and all of this node’s descendants. The tree s could also be considered as a subtree of itself.
Example 1:
Given tree s:
Return true, because t has the same structure and node values with a subtree of s.
Example 2:
Given tree s:
Return false.
很简单的一个递归算法。如果当前节点数值一样,那么先判断是否identical,如果不是,考虑left, 考虑right是否和target tree存在subset关系。
C++
Java
Given a string S and a string T, count the number of distinct subsequences of S which equals T.
A subsequence of a string is a new string which is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, “ACE” is a subsequence of “ABCDE” while “AEC” is not).
Here is an example:
S = “rabbbit”, T = “rabbit”
Return 3.
dp[i][j]表示的是s[0,i]和t[0,j]的匹配答案。
递推关系可以分为s[i] == t[j] 和不等的两种情况
如果相等,那么既可以是包括i, 那么就是需要知道(i-1,j-1)的结果;也可以是不包括j, 那么就需要知道(i -1, j)的结果
如果不相等,只要(i - 1, j)就可以了。
C++
Java
Given an integer array with all positive numbers and no duplicates, find the number of possible combinations that add up to a positive integer target.
Example:
Note that different sequences are counted as different combinations.
Therefore the output is 7.
Follow up:
What if negative numbers are allowed in the given array?
How does it change the problem?
What limitation we need to add to the question to allow negative numbers?
dp[i]表示的是target为i时一共的解法。
对于如果target较大的话,可以先把nums排一下序。然后在内层循环里面当i<num的时候直接break就可以了。
follow up:如果负数被允许的话,解答可能是infinite。比如[-1,1],target为1的情况。
这个时候需要限制比如每个元素用几次之类的。
Java
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of longest increasing subsequence.
For example,
Given [10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18],
The longest increasing subsequence is [2, 3, 7, 101], therefore the length is 4. Note that there may be more than one LIS combination, it is only necessary for you to return the length.
Your algorithm should run in O(n2) complexity.
Follow up: Could you improve it to O(n log n) time complexity?
经典dp, dp[i]是到第i个数字的最大递增subsequence, 那么dp[i] = Max(dp[k1], dp[k2], dp[k3]…) + 1, nums[i] > nums[kn]
C+,
Java
解释参考leetcode 的答案解释:
|
|
Given an Android 3x3 key lock screen and two integers m and n, where 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 9, count the total number of unlock patterns of the Android lock screen, which consist of minimum of m keys and maximum n keys.
Rules for a valid pattern:
Each pattern must connect at least m keys and at most n keys.
All the keys must be distinct.
If the line connecting two consecutive keys in the pattern passes through any other keys, the other keys must have previously selected in the pattern. No jumps through non selected key is allowed.
The order of keys used matters.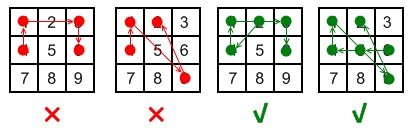
Explanation:
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 7 | 8 | 9 |
Invalid move: 4 - 1 - 3 - 6
Line 1 - 3 passes through key 2 which had not been selected in the pattern.
Invalid move: 4 - 1 - 9 - 2
Line 1 - 9 passes through key 5 which had not been selected in the pattern.
Valid move: 2 - 4 - 1 - 3 - 6
Line 1 - 3 is valid because it passes through key 2, which had been selected in the pattern
Valid move: 6 - 5 - 4 - 1 - 9 - 2
Line 1 - 9 is valid because it passes through key 5, which had been selected in the pattern.
Example:
Given m = 1, n = 1, return 9.
这题一拿到感觉是dp或者是dfs的题目。用dp想不出状态方程看来只能用dfs试一下。
dfs的话最核心的思想就是每次往目标前进一步,如果成功则再继续探寻。
这个问题的一部是要看上一步和当前一步是否构成一个合适的movement.
一定是:
1. 相邻的
2. 对线的
3. 不相邻但是当中的数字已经被访问过了
那么用一个数组维护访问过的数字,同时维护一个上次访问的数字和当前的数字,以便判断一个move是否合适。
对于每一个数字进行dfs遍历,每前进一步就把所剩的步数-1.
C++
Java
由于可能的跳跃是有限的,可以用一个table来存储合法的跳跃path。这样可以简化很多检查一个move是否合法的code。
每次DFS的时候从一个点开始,找出可能的path。同时利用对称性,1,3,7,9是一样的;2,4,6,8是一样的。5单独一个。
|
|
You are given a string, s, and a list of words, words, that are all of the same length. Find all starting indices of substring(s) in s that is a concatenation of each word in words exactly once and without any intervening characters.
For example, given:
s: “barfoothefoobarman”
words: [“foo”, “bar”]
You should return the indices: [0,9].
(order does not matter).
也是滑动窗口的思路,第一层循环是对于起始点的遍历。起始点可以从0到word的长度-1。
之后就是一个词一个词的向右进。同时统计每一个词出现的次数。
C++
Java
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring T that contains at most k distinct characters.
For example, Given s = “eceba” and k = 2,
T is “ece” which its length is 3.
滑动窗口的解法。
C++
Java
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring T that contains at most 2 distinct characters.
For example, Given s = “eceba”,
T is “ece” which its length is 3.
这题是sliding window的一个例题。要掌握一下模板。这题和另一题at most k distinct characters的解法一致。
主要的思路就是维护一个hashmap存取每一个元素出现的次数,如果为1的话,就说明是新入的元素,总个数要+1
同时维护一个start指针来标记左面的边界,每次找到一个符合标准的答案时,更新最长的长度。
C++
Java